From Workshop to World Stage: Top CNC Machine Uses That Power Everyday Life
Walk into any modern workshop, and you’re bound to find at least one humming, whirring CNC machine at work. Whether...
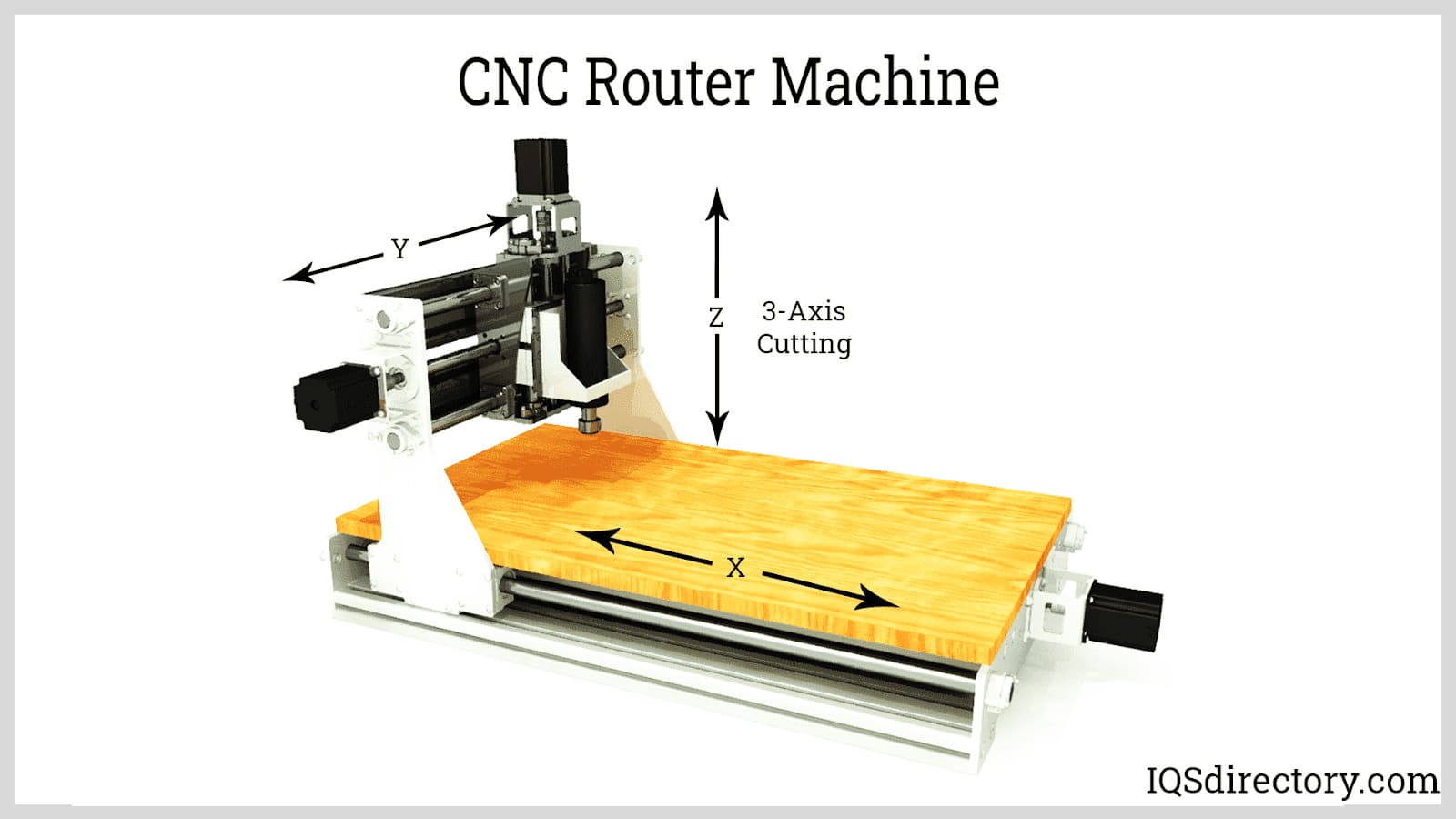
Walk into any modern workshop, and you’re bound to find at least one humming, whirring CNC machine at work. Whether shaping metal, carving wood, or drilling precise holes into plastic, CNC machines—short for Computer Numerical Control machines—have revolutionized manufacturing with speed, precision, and repeatability.
But while many associate CNC machines with industrial settings, their uses extend far beyond factories. From fashion and furniture to aerospace and agriculture, CNC machining has quietly become the backbone of production across nearly every sector.
This article explores the many real-world CNC machine uses and the impact they have on how we live, move, and create.
What Is a CNC Machine?
At its core, a CNC machine is a tool operated by computer instructions rather than human hands. These machines interpret a digital file (usually a CAD drawing or 3D model) and translate it into a series of precise movements. The result? Parts that are accurate, consistent, and fast to produce, regardless of complexity.
CNC machines come in many forms, including:
- CNC Milling Machines
- CNC Lathes
- CNC Routers
- CNC Laser Cutters
- CNC Plasma Cutters
- CNC EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining)
These machines can handle materials such as aluminum, steel, plastics, wood, foam, and even carbon fiber composites.
1. CNC in Daily Consumer Goods
You probably touch dozens of CNC-machined items every single day without realizing it. From your smartphone casing to the metal zippers on your bag, CNC plays a vital role in the mass production of consumer goods.
Examples:
- Precision watch components
- Eyeglass frames
- Smartphone chassis
- Laptop covers
- Gaming console components
With CNC, manufacturers ensure tight tolerances, sleek finishes, and fast turnarounds—even when dealing with tiny parts at high volume.
2. Precision Automotive Manufacturing
In the automotive industry, accuracy is critical. Cars are complex machines with thousands of parts, many of which are CNC-machined for consistency and reliability.
Common CNC Automotive Applications:
- Engine blocks and pistons
- Brake rotors and calipers
- Gearbox housings
- Suspension arms
- Dashboard panels and trim pieces
CNC machines also assist in custom automotive projects, such as performance tuning and aftermarket modifications.
3. Aerospace: Where Precision Meets Performance
The aerospace industry is perhaps the most demanding when it comes to manufacturing tolerances. In this field, CNC machines are essential for creating lightweight yet ultra-strong components.
Aerospace CNC Uses:
- Jet engine parts
- Fuel nozzles
- Aircraft skin panels
- Turbine blades
- Cabin interior elements
5-axis CNC machines are especially valuable here, allowing manufacturers to cut complex, contoured parts from exotic materials like titanium.
4. Healthcare and Medical Equipment
CNC machining isn’t just for machines—it helps save lives too. The medical field requires sterile, precise, and durable components, all of which CNC can produce efficiently.
CNC in Healthcare:
- Orthopedic implants (e.g., hip and knee joints)
- Dental crowns and braces
- Surgical tools and instruments
- Customized prosthetics
- Hearing aids and device housings
The ability to make patient-specific items has made CNC a cornerstone of modern medical manufacturing.
5. Agriculture and Heavy Equipment
CNC machines help build the powerful machinery used in farming, construction, and mining. These industries depend on durable, precisely-machined parts to operate in rough environments.
Applications:
- Tractor parts and engine components
- Hydraulic fittings
- Drive shafts and gears
- Construction vehicle components
- Custom farming equipment attachments
Because CNC parts are repeatable and reliable, they help reduce downtime in large-scale operations.
6. Architectural and Interior Design
Architects and designers use CNC machines to bring creativity to life through intricate patterns, custom features, and functional elements.
In This Field, CNC Is Used For:
- Carved wall panels
- Custom furniture pieces
- Decorative metalwork
- Unique cabinetry
- Signage and branding installations
CNC routers and laser cutters make it easy to turn a digital design into a finished product with complex detailing and perfect symmetry.
7. Fashion, Jewelry, and Accessories
CNC machining isn’t limited to hard industries—it also has a growing presence in fashion and jewelry design. Designers use CNC machines to create unique, wearable works of art.
CNC Enables:
- Jewelry molds and wax carvings
- Precision-cut metals and stones
- Custom belt buckles, buttons, and clasps
- 3D engraved fashion accessories
The ability to quickly produce detailed parts in small quantities makes CNC a favorite for boutique brands and artists alike.
8. Education and Training
CNC machines are increasingly found in technical schools, colleges, and maker spaces, where students learn not just machining, but digital design, programming, and problem-solving.
Students Learn to:
- Operate CNC mills and lathes
- Create G-code or use CAM software
- Understand toolpaths and tolerances
- Prototype new inventions
With hands-on experience, learners become ready for roles in engineering, product development, and advanced manufacturing.
9. Rapid Prototyping and Product Testing
CNC machines are often used during the research and development phase of a product’s lifecycle. Before mass production begins, CNC helps create functional prototypes.
CNC Advantages in R&D:
- Allows rapid iteration
- Uses real materials, not plastic models
- Produces testable, functional parts
- Reduces development time
Companies can go from concept to working model in days, allowing faster decision-making and market testing.
10. Tool and Die Making
To build the tools that make everything else, you need CNC machining. Tool and die shops rely on CNC for fabricating molds, dies, and jigs used in other manufacturing processes.
Key Uses:
- Injection molds for plastics
- Dies for stamping and forging
- Precision jigs and fixtures
- Gauges and measuring tools
These parts must be perfect—because they influence every other product that passes through them.
Final Thoughts: CNC Machines as Invisible Innovators
CNC machines may not be flashy, but their impact is massive. They’re the unsung heroes of modern production, quietly shaping the cars we drive, the tools we use, the phones we carry, and even the medical devices that keep us healthy.
Their uses span industries, from agriculture to aerospace, fashion to furniture. And with continued advancements in automation, software, and materials, CNC machine uses are only growing more powerful.
Whether you’re a product designer, factory owner, student, or artist—if you’re making something, chances are a CNC machine can help you make it better, faster, and with precision you can trust.







