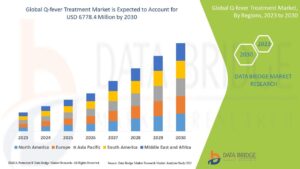
Q-Fever Treatment Market: Addressing a Silent Zoonotic Threat
Introduction The Q-Fever Treatment Market is emerging as a significant focus within the broader infectious disease therapeutics space. As zoonotic diseases garner...
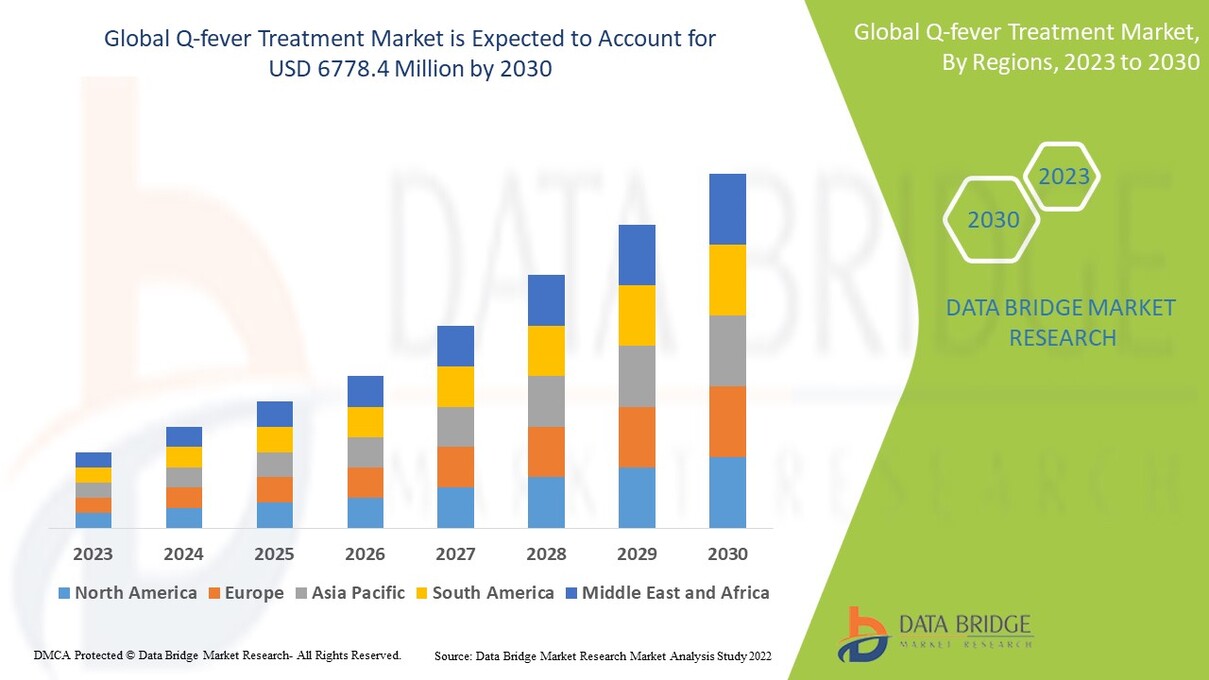
Introduction
The Q-Fever Treatment Market is emerging as a significant focus within the broader infectious disease therapeutics space. As zoonotic diseases garner more attention in the wake of global health events, Q fever—caused by the highly infectious bacterium Coxiella burnetii—is stepping out of obscurity. Although it primarily affects livestock such as cattle, sheep, and goats, humans can contract the illness through inhalation of contaminated particles, often leading to debilitating symptoms and, in chronic cases, life-threatening complications like endocarditis. The treatment landscape is evolving with intensified research, increased awareness, and strategic health responses targeting early intervention, vaccine development, and long-term monitoring.
The Evolution of Q-Fever Management
Initially classified as an occupational hazard restricted to livestock handlers, abattoir workers, and farmers, Q fever is now being acknowledged as a potential public health emergency, particularly in densely populated agricultural zones. The earliest recognized outbreak in Queensland, Australia, in the 1930s paved the way for the term “Q,” short for “Query,” to be used until the disease’s etiology was discovered.
The management of Q fever has historically centered on doxycycline, which remains the gold-standard antibiotic for acute infections. However, chronic cases—especially involving cardiac or vascular tissues—require prolonged combination therapies with hydroxychloroquine and follow-up serological testing. The last decade has brought renewed focus on developing animal and human vaccines, personalized treatment regimens, and computational modeling to predict outbreak behavior based on environmental and agricultural patterns.
Source : https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-q-fever-treatment-market
Market Trends
The Q-Fever Treatment Market is undergoing pivotal transformation driven by modern healthcare demands and technological evolution:
- Advancements in rapid diagnostic tools are enabling early and more accurate detection, even during asymptomatic phases.
- Digital disease surveillance platforms are helping map Q fever incidence with higher granularity, aiding public health planning.
- Development of next-generation vaccines targeting both humans and livestock is accelerating, with several candidates in clinical pipeline phases.
- Innovations in point-of-care testing and mobile clinics are improving treatment accessibility in rural and underserved regions.
- Global One Health initiatives are encouraging integrated approaches, tying together animal health, human health, and environmental science to combat zoonotic transmission chains.
Challenges
Despite technological progress, the Q-Fever Treatment Market is encumbered by persistent challenges:
- Lack of global standardization in diagnostic criteria and testing protocols leads to inconsistencies in clinical decision-making.
- Many healthcare professionals remain unfamiliar with Q fever, resulting in diagnostic delays and potential progression to chronic forms.
- The economic impact on livestock industries creates hesitancy in vaccination campaigns and disease disclosure due to concerns over trade restrictions.
- Chronic Q fever remains a major clinical hurdle, with few treatment options beyond extended antibiotic regimens that often carry toxicities and adherence issues.
- Cultural barriers and misinformation about zoonotic diseases in farming communities hinder health education and treatment-seeking behavior.
Market Scope
The Q-Fever Treatment Market is broad in its application and stakeholder engagement. It encompasses:
- Pharmacological therapies including first-line antibiotics, adjunctive therapies, and research into antimicrobial resistance mitigation.
- Veterinary interventions that include livestock vaccination, breeding management, and microbial surveillance in farm environments.
- Diagnostic innovations, particularly multiplex PCR and serology platforms, enabling faster pathogen identification in clinical and veterinary settings.
- Health informatics and biosurveillance infrastructure that inform policy actions and emergency preparedness.
- Academic and commercial research partnerships focused on longitudinal cohort studies, vaccine development, and host-pathogen interaction mapping.
In recent years, the market has also extended into bioterrorism preparedness, as Coxiella burnetii is classified by the CDC as a potential Category B biological threat, warranting additional investment in national stockpiles and secure treatment protocols.
Market Size
The Q-Fever Treatment Market is steadily expanding due to heightened awareness, investments in zoonotic disease control, and evolving global health priorities. Forecast models indicate that the market will continue to grow significantly over the next decade as new treatment options gain regulatory approval and as public health agencies allocate more resources toward rural health outreach and agricultural disease management.
Countries with large livestock industries, such as Australia, Brazil, the United States, and parts of Europe, remain primary contributors to market demand. Simultaneously, developing nations in Asia and Africa are expected to play a growing role in market expansion due to increased zoonotic surveillance, donor funding, and health system strengthening programs aimed at integrated epidemic prevention.
Factors Driving Growth
A confluence of factors is accelerating the trajectory of the Q-Fever Treatment Market:
- Urban expansion into livestock-rich environments increases human exposure to animal pathogens.
- Climate change is disrupting traditional ecosystems and influencing pathogen transmission rates, extending Q fever risk into previously unaffected areas.
- Strengthened public health infrastructure, especially post-pandemic, is driving national-level infectious disease preparedness programs that include Q fever.
- Cross-sector collaboration between agriculture, biotech, government, and global health NGOs is fueling both treatment accessibility and innovation.
- Expanded academic interest and funding into Q fever’s immunological mechanisms and pathogen genetics is leading to better-targeted therapies and more responsive treatment models.
In addition, the globalization of food supply chains and increased livestock movement are prompting international cooperation on surveillance, regulation, and early intervention strategies for zoonotic threats.
Conclusion
The Q-Fever Treatment Market has moved beyond the shadows of neglect into the broader spotlight of public health innovation. As zoonoses rise to the forefront of pandemic preparedness and disease control agendas worldwide, Q fever presents both a challenge and an opportunity—a challenge due to its capacity for silent transmission and chronic manifestation, and an opportunity to build resilient, proactive healthcare and agricultural systems capable of managing zoonotic threats at their source.
By enhancing global surveillance, diversifying treatment options, developing safe and effective vaccines, and ensuring equitable access to care for affected populations, the global health community can significantly reduce the burden of Q fever. More importantly, the sustained evolution of this market underscores a broader imperative: that the boundary between animal health and human health is no longer divisible. Addressing that intersection with clarity, science, and collaborative action will define the success of the Q-Fever Treatment Market in the years to come.